Fundamental Rights, Directive Principles, Fundamental Duties, Citizenship, and Constitutional Amendments | Mock Test
The Indian Constitution provides for Fundamental Rights (Articles 12–35) that guarantee individual freedoms and equality, such as the rights to equality, freedom, and constitutional remedies. Directive Principles of State Policy (Articles 36–51) are non-enforceable guidelines for the government to establish social and economic justice. Fundamental Duties (Article 51A), added by the 42nd Amendment, are moral obligations for citizens like respecting the Constitution and protecting the environment. Citizenship (Articles 5–11) defines who is an Indian citizen and how citizenship can be acquired or lost. Constitutional Amendments (Article 368) allow the Constitution to be updated, with key amendments like the 42nd, 44th, and 73rd shaping Indian democracy.
Result:
1
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഭരണഘടനയിൽ തുല്യതയുടെ അവകാശം ഉറപ്പുനൽകുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
2
ആർട്ടിക്കിൾ 19 പ്രകാരമുള്ള സംസാരസ്വാതന്ത്ര്യവും പ്രകടനവും യാതൊരു നിയന്ത്രണവുമില്ലാതെ പൂർണമായ അവകാശമാണോ?
3
ജീവനും വ്യക്തിഗത സ്വാതന്ത്ര്യവും സംരക്ഷിക്കുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
4
മതം, വർഗം, ജാതി, ലിംഗം, ജനനസ്ഥലം എന്നിവയുടെ അടിസ്ഥാനത്തിൽ വിവേചനം തടയുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
5
അസ്പൃശ്യത നിർമാർജനം ചെയ്യുന്നതിന് ഉറപ്പുനൽകുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
6
മൗലികാവകാശങ്ങൾ നടപ്പിലാക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള നിയമപരമായ പരിഹാരാവകാശം ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ് ഉറപ്പുനൽകുന്നത്?
7
നിർദേശക തത്ത്വങ്ങൾ ഇന്ത്യൻ ഭരണഘടനയിൽ ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളുകളിലാണ് അടങ്ങിയിരിക്കുന്നത്?
8
നിർദേശക തത്ത്വങ്ങൾ നിയമപരമായി നടപ്പിലാക്കാൻ കഴിയുന്നവയാണോ?
9
വിദ്യാഭ്യാസം, തൊഴിൽ, പൊതുസഹായം എന്നിവയ്ക്കുള്ള അവകാശം പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
10
പിന്നോക്ക വിഭാഗങ്ങളുടെ ക്ഷേമം പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള നിർദേശം ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളിലാണ്?
11
ഏകീകൃത സിവിൽ കോഡ് നടപ്പിലാക്കാൻ സംസ്ഥാനത്തെ പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
12
പൊതുജനങ്ങളുടെ പോഷണനിലവാരവും ജീവിതനിലവാരവും ഉയർത്താൻ ശ്രമിക്കണമെന്ന് നിർദേശിക്കുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
13
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഭരണഘടനയിൽ മൗലിക കടമകൾ ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളിലാണ് വിവരിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നത്?
14
മൗലിക കടമകൾ നിയമപരമായി നടപ്പിലാക്കാൻ കഴിയുന്നവയാണോ?
15
ഏത് മൗലിക കടമ പൗരന്മാരോട് ദേശീയ പതാകയെയും ദേശീയ ഗാനത്തെയും ബഹുമാനിക്കാൻ ആവശ്യപ്പെടുന്നു?
16
പൗരന്മാർ പരിസ്ഥിതി സംരക്ഷിക്കണമെന്ന് ആവശ്യപ്പെടുന്നത് ഏത് മൗലിക കടമയാണ്?
17
ശാസ്ത്രീയ മനോഭാവവും മാനവികതയും വളർത്തണമെന്ന് പൗരന്മാരോട് ആവശ്യപ്പെടുന്നത് ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളാണ്?
18
ഏത് മൗലിക കടമ പൗരന്മാരോട് ഭരണഘടനയെ അനുസരിക്കാനും അതിന്റെ ആദർശങ്ങളെ ബഹുമാനിക്കാനും ആവശ്യപ്പെടുന്നു?
19
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഭരണഘടനയിൽ പൗരത്വവുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട വ്യവസ്ഥകൾ ഏത് ആർട്ടിക്കിളുകളിലാണ്?
20
ഇന്ത്യയിൽ ജനിച്ച ഒരു വ്യക്തിക്ക് പൗരത്വം ലഭിക്കുന്നത് ഏത് അടിസ്ഥാനത്തിലാണ്?
21
ഇന്ത്യൻ പൗരത്വ നിയമം അവസാനമായി ഭേദഗതി ചെയ്തത് എപ്പോഴാണ്?
22
പൗരത്വവുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട വ്യവസ്ഥകൾ നടപ്പിലാക്കാൻ ആർക്കാണ് അധികാരം?
23
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഭരണഘടന പ്രകാരം ഒരു വ്യക്തിക്ക് ഇന്ത്യയുടെയും മറ്റൊരു രാജ്യത്തിന്റെയും പൗരത്വം ഒരേസമയം വഹിക്കാൻ കഴിയുമോ?
24
ഇന്ത്യൻ പൗരത്വം ലഭിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഒരു മാർഗമായി ഭരണഘടന അംഗീകരിക്കുന്നത് എന്താണ്?
25
42-ാം ഭേദഗതി, "മിനി ഭരണഘടന" എന്നറിയപ്പെടുന്നത്, ഏത് വർഷമാണ് നടപ്പിലായത്?
26
42-ാം ഭേദഗതി പ്രകാരം ഭരണഘടനയിൽ എന്താണ് ചേർത്തത്?
27
86-ാം ഭേദഗതി, സൗജന്യ വിദ്യാഭ്യാസത്തിനുള്ള അവകാശം, ഏത് വർഷമാണ് ചേർത്തത്?
28
ആർട്ടിക്കിൾ 368 പ്രകാരം ഭരണഘടന ഭേദഗതി ചെയ്യാൻ പാർലമെന്റിന് അധികാരം നൽകുന്നത് ഏത് ഭാഗത്താണ്?
29
42-ാം ഭേദഗതി ഭരണഘടനയുടെ ആമുഖത്തിൽ ഏത് വാക്കുകൾ ചേർത്തു?
30
24-ാം ഭേദഗതി, പാർലമെന്റിന്റെ ഭേദഗതി അധികാരത്തെ ശക്തിപ്പെടുത്തിയത്, ഏത് വർഷമാണ്?
Downloads: loading...
Total Downloads: loading...
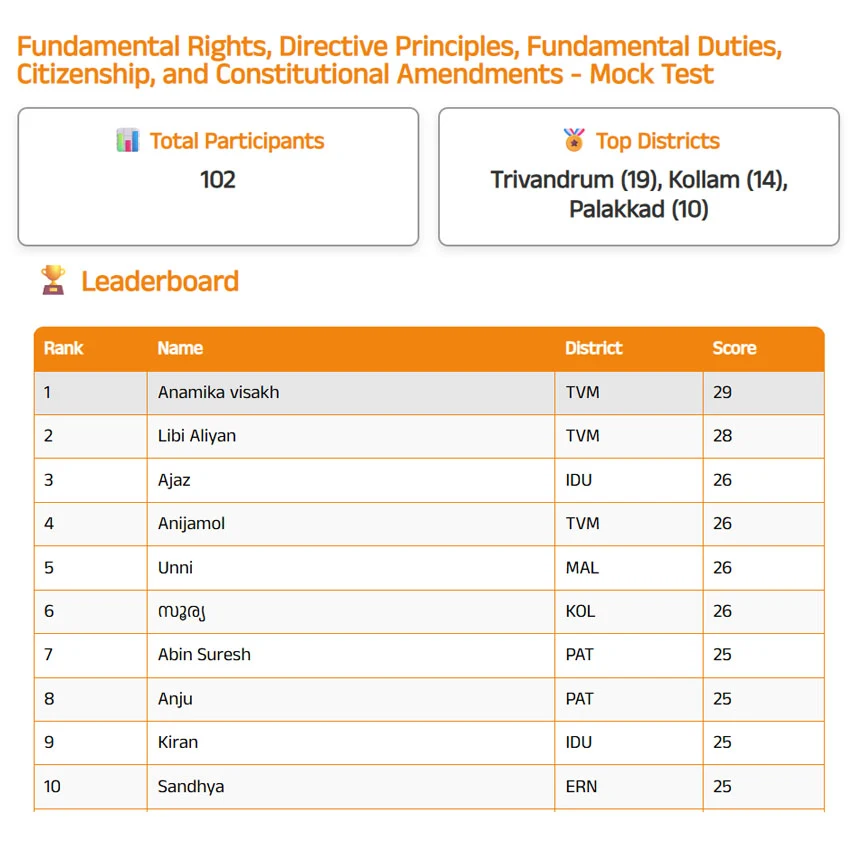
Leaderboard of the quiz Conducted on 29 Jun 2025















0 Comments